In an increasingly interconnected world, the significance of robust cybersecurity cannot be overstated. The global landscape has witnessed a surge in cyberattacks, driven primarily by financial motivations. As organizations and governments worldwide grapple with the fallout of these attacks, it’s crucial to assess the state of cybersecurity in our own backyard here in Ethiopia. Especially in light of the recent push to grow the nation’s digital economy, tandem attention must be paid to the protection of this new frontier.

The Global Cybersecurity Landscape
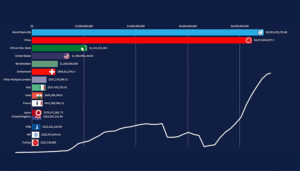
The motivation for cybercriminals has, more often than not, been financial gain. Organizations worldwide not only bear the financial burden of retrieving lost data but also suffer operational disruptions due to cybercrimes. The global average cost of a data breach stands at a staggering 4.35 million U.S. dollars, with variances influenced by regions, organization sizes, and industries. The relentless wave of cyber threats has underscored the critical importance of cybersecurity in the digital age.
Driven by a heightened awareness of data risks and evolving threats, the global cybersecurity market has experienced substantial growth. From $83.32 billion in 2016, its revenue is projected to reach approximately $166 billion by 2023. What was once considered the domain of IT departments is now integral to top-level strategic planning across organizations. It can easily be argued that the sub-Saharan region may not be walking toe-to-toe with the global trendsetters, so it is wise to contextualize the conversation.
A Neighbor’s Experience
In neighboring Kenya, the alarm bells have been ringing loud and clear. The country witnessed a staggering 860 million cyberattack incidents in the past year, according to the communications regulator. These attacks, characterized by their increasing frequency, sophistication, and scale, have targeted Kenya’s critical information infrastructure. To put this in perspective, just four years ago, Kenya faced 7.7 million cyberattacks, a relatively modest number for the nation, highlighting the exponential growth in cyber threats.
Ethiopia’s Cybersecurity Landscape
Now, let’s turn our attention to Ethiopia, where the Information Network Security Administration (INSA) has been on the front lines of the battle against cyber threats. In the concluded Ethiopian Fiscal Year, INSA reported thwarting a mere 6,768 cyberattack attempts against the country. It was also reported that INSA saved Ethiopia a whopping 23.2 billion Birr by successfully mitigating these attacks.
These numbers fall far below the global (or even regional) stats. Some of this can be ascribed to Ethiopia’s late boom in the digital space. Ethiopia has witnessed significant enhancements in its telecommunications and mobile network infrastructure. There is promising growth; at the beginning of 2023, Ethiopia’s internet penetration rate stood at 16.7%; it is estimated that there’s been a 2.6% increase in the number of internet users in Ethiopia between 2022 and 2023 alone. The potential for economic growth through the modernization of digital payment systems is substantial, with the potential to increase annual GDP by 3% in emerging nations. In the case of Ethiopia, specifically, it is forecasted that digital transactions will grow nine-fold by 2025 from what it was in 2020. For contrast, in neighboring Kenya, the ICT sector has experienced consistent annual growth of 10.8% since 2016. It is projected that the digital economy in Kenya will make up 9.24% of the country’s GDP by 2025. To put this into perspective, in 2006, only 26.7% of the Kenyan population had access to formal financial services.
INSA itself is a formidable organization up to the task of girding the nation from potential susceptibilities, but it is not without its flaws or risks. Not too long ago, the agents of the organization were hacked, exposing the inner weakness of the organization. It was reported that “[…] Big databases usually have their data protected and encrypted (in case someone breaks in), this one [INSA] didn’t and had common passwords easy to decrypt…”
The organization is tasked with a significant responsibility: addressing the risks stemming from the overall low levels of digital literacy in the country. However, it’s worth noting that even established organizations, universities, and government agencies continue to rely on personal email services like Yahoo or Gmail for official communication. This practice is particularly concerning given that human error is responsible for a staggering 82% of global data breaches. Examples of such errors include sharing passwords, neglecting patch management, clicking on unsafe URLs, and accessing organizational data through personal devices – all of which pose significant security threats, many of which could be mitigated through basic digital literacy training.
Considering these factors, a total of 6,959 attacks over the span of a year appears to be significantly lower than expected, possibly indicating a cautious public notice at best or a potential oversight at worst.
What Do We Know About These Attacks?
INSA Director-General Solomon Soka revealed that a total of 6,959 cyberattack attempts were made against Ethiopia during the past year. Of these attempts, 6,768 were foiled, while 191 succeeded. The targets encompassed a range of sectors, including financial institutions, security organizations, media outlets, healthcare, and educational institutions, as well as various government ministries and regional offices.
The types of cyberattacks attempted against Ethiopia included service interruptions, infrastructure penetrations, and website attacks. According to Cisqo, a multinational digital communications technology conglomerate, the most common forms of cyberattacks are malware, phishing, man-in-the-middle-attacks, and denial-of-service-attacks.
Hacking the Future
As Ethiopia navigates the ever-evolving digital landscape, the role of organizations like INSA becomes increasingly vital. The recent successes in thwarting cyberattacks and preserving financial resources may be promising but they are also a wake-up call. The evolving nature of cyber threats demands continued vigilance, collaboration, and innovation to safeguard Ethiopia’s digital future.
The proactive efforts of organizations like INSA are commendable, but they also serve as a reminder that cybersecurity is an ongoing battle that requires constant adaptation to local contexts and preparedness in the face of evolving risks. As Ethiopia continues its digital transformation, the nation’s ability to secure its digital sovereignty will be crucial for its future success, within and outside the realm of the much-anticipated boom of the digital economy.










One Response
¡Gran artículo sobre la frontera digital y los desafíos que presenta! Es fascinante explorar cómo la tecnología está transformando nuestras vidas y la forma en que interactuamos. A medida que avanzamos en esta era digital, es crucial estar preparados para enfrentar los retos que surgen. Además, para aquellos interesados en mejorar su estrategia en línea, les recomiendo este artículo sobre cómo crear contenido SEO amigable: Telkom University Jakarta. ¡Gracias por compartir información tan relevante!