Economic expansion and export capacity are closely linked, as the exporting sector significantly contributes to a country’s stability and income distribution. The Ethiopian government has implemented several measures to boost its export sector, such as devaluing the national currency, eliminating export taxes, and providing subsidies. These changes have promoted competitiveness and profitability in international markets, generating foreign currency for both the public and private sectors.
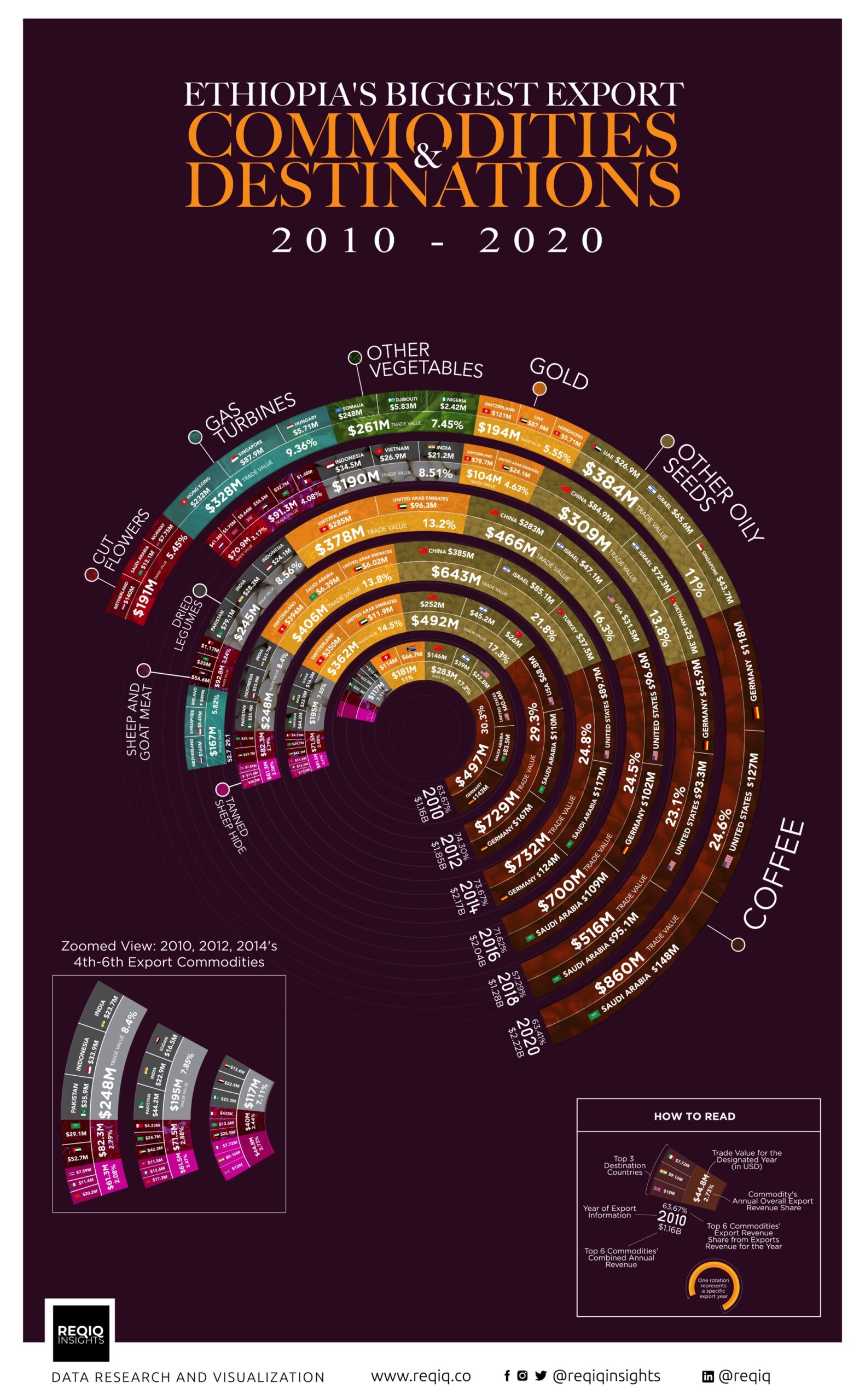
Recent industrialization efforts in Ethiopia have resulted in new industrial parks, flourishing local products, and increased opportunities for import-export businesses. However, the export economy remains heavily reliant on a limited number of commodities, making it vulnerable to price shocks. Export diversification is thus crucial for ensuring macroeconomic stability and competitive foreign exchange rates.
Ethiopia has made promising strides in diversifying its exports, with sectors like textiles showing optimism. This progress is further supported by agreements and partnerships with countries like China, which has become a major trading partner and source of foreign direct investment, loans, and development assistance. Chinese investments have contributed to infrastructure development, industrial parks, and manufacturing, enabling Ethiopia to diversify its economy, create jobs, and boost exports. Nonetheless, concerns about debt sustainability, dependency, and environmental and social impacts have emerged due to this relationship.
Exports can play a significant role in shaping a country’s foreign relations. Engaging in international trade allows nations to strengthen their diplomatic ties and influence global policies. By establishing a strong export sector, Ethiopia can leverage its economic connections to foster mutually beneficial relationships with trading partners, enhance regional cooperation, and promote its interests on the global stage. Moreover, increased trade fosters interdependence between countries, which can contribute to peace and stability in the region. As Ethiopia continues to diversify its exports and forge new partnerships, it will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of international diplomacy and enhance its standing in the global community.
To sustain growth and development, Ethiopia will likely continue to focus on export diversification, infrastructure development, human capital, regional integration, and addressing political challenges. Prioritizing these areas will help ensure political stability, inclusive economic growth, and the country’s future prosperity.
Over the past decade, Ethiopia has seen a gradual increase in export activities, with major products including coffee, oilseeds, livestock, flowers, textiles, and garments. The growth of these sectors is attributed to favorable government policies, foreign investment, and industrial park development. Despite these advancements, Ethiopia’s export performance has yet to reach its full potential due to challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, limited financing, and a shortage of skilled workers. However, the growing manufacturing sector and value-added exports signal a successful transition towards industrial development, which is vital for Ethiopia’s economic growth and job creation.










